Dumb or not, you can learn the basics of search engine optimization (SEO) in 30 minutes.
This "SEO for dummies" guide will teach you:
- What SEO is and how search engines work
- How to do keyword research
- The fundamentals of SEO and how you can rank in the top results on Google
I've been doing SEO for over 10 years and my sites have gotten millions of organic visits from Google.
This guide shares everything I've learned in that time, simplified so anyone can understand it.
Quickstart: How to Use This Guide
This SEO for dummies guide is written for the complete beginner. The regular text in this guide is very easy to understand.
However, there are some complex topics that may go over your head right now. I've included these more "advanced" search engine optimization tips so you can fully understand the subject.
That said, these more advanced topics are not necessary for you to know to get started, and you can skip them if you're not ready to dive in that deep!
To help you navigate these complex topics, I've placed the icon you see to the left next to any "big brain" topics that are more advanced but you don't need to know right away.
I definitely recommend reading them still if you want to master SEO, but don't feel pressured to learning them right away if it's too much to take in right now.
I hope this helps — now let's get to it!
Lesson 1: What Is SEO?
Search Engine Optimization (SEO) is the art of tweaking your website in a way that helps search engines like Google index and display your site in their search results.
SEO typically involves tasks like:
- Researching keywords you want to rank for.
- Creating content that matches the search intent of those keywords.
- Improving your site's navigation structure and loading speeds.
- Getting other websites to link back to your site from their site (AKA backlinks).
If you don't understand anything I just said, don't worry — I will clarify what each of these tasks means and how to do them in the following sections.
In a nut shell, search engine optimization means creating high-quality content that both your readers as well as Google's robots want to see. And I'm going to teach you exactly how to do that.
But first, why should you even care?
Lesson 2: Why Bother Learning SEO?
SEO is one of the best ways to create passive income and business growth.
Why?
Because once you rank on page one for a keyword, you tend to keep those rankings for a long time. Years, even.
I should know — both my own sites and my client's sites have held many of their rankings for the last 5+ years, and will likely continue to do so for many more years to come (assuming we keep the pages up-to-date and relevant).
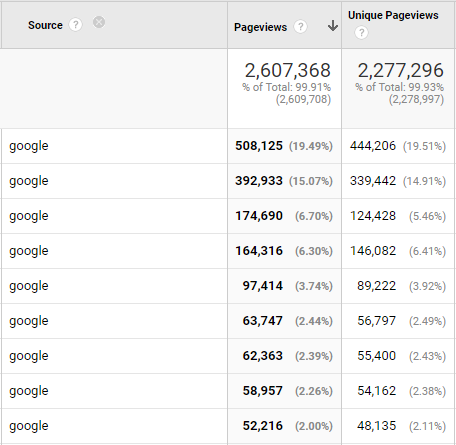
Here's my Google site traffic from the last 12 months to just one of my websites:
In other words, your SEO efforts can bring you targeted traffic consistently with little maintenance... for free! Need I say more?
Lesson 3: SEO Terms and Phrases
Before we dive into SEO for dummies, let me define some common terms & phrases I'll be using throughout this article:
- Domain Authority (DA): This is a number from 0-100 that Moz (an SEO software company) created to give you an idea of how "authoritative" your website is in Google's eyes. It doesn't actually have anything to do with ranking on Google, but it can give you an idea of how you fare compared to your competition. Theoretically, the higher this number, the easier it is for your website to rank well in Google. You raise this number by building links to your website (more on that later).
- Domain Rating (DR): This is Ahrefs' version of DA. It is basically the same thing, just tweaked according to Ahrefs' idea of authority. I use Ahrefs a lot, so I'll be using this metric more often in this guide.
- Robots.txt: This is a file you can create to tell Google which pages on your website to index in their search results and which to ignore. More on this later.
- XML Sitemap: This is a file or page on your website that contains links to every page on your website. It's used to help Google (and sometimes your visitors) more easily crawl and navigate your website.
- Crawling: When I refer to Google "crawling" your website, what I mean is that Google's search robots (referred to as "spiders") are scanning your pages in order to index them.
- Indexing: Think of indexing like a filing cabinet. Google's spiders are crawling your website and indexing your pages into the proper "file", i.e. search results. When your page gets indexed, it means Google may now display your content in the organic search results. However, just because your site is indexed, doesn't mean you will rank in the top 10 or even top 50 results. It just means your content can be displayed in the results.
- Spiders: This is what search engine's crawling robots are referred to as. Google's "spiders" are the "robots", or pieces of code, that allow them to read and index your pages.
That's all there is to it! If you have any questions about these terms, feel free to leave a comment below and I'll do my best to explain further.
Lesson 4: How Do Search Engines Work?
Search engines operate using three primary functions: crawling, indexing, and ranking. Let's break down how these work.
Crawling:
- Crawling is the first step in the process, where search engines send out a team of robots (often called spiders or crawlers) to find new and updated content.
- Content can vary — it could be a webpage, an image, a video, a PDF, etc. — anything that can be discovered by a link.
- The crawlers navigate the web by following links, going from one page to another and collecting data about those pages to bring back to the search engine’s servers.
Indexing:
- After a page is crawled, the information is then indexed, or stored, in a huge database.
- Indexing involves analyzing the content (text, images, etc.) of each page and storing it in a way that allows it to be efficiently retrieved. This includes understanding what the page is about, what keywords it contains, its relevance to various topics, and more.
- Not all crawled pages will be indexed. For example, pages with duplicate content, broken links, or those blocked by robots.txt files might be excluded.
Ranking:
- When a user performs a search, the search engine sifts through its indexed pages to provide the most relevant and useful results.
- Ranking is the process by which the search engine decides which pages appear first in the search results. This determination is based on various factors, including (but not limited to) the keywords used in the query, the relevance and usability of pages, the expertise and credibility of sources, and the location and settings of the user.
- The specific ranking factors and their importance can vary between search engines and evolve over time. For example, Google uses a complex algorithm that considers over 200 factors to rank pages and is updated up to 2,000 times per year.
Search engines are constantly updating and refining their processes to better understand and navigate the ever-growing and changing content on the internet.
The goal of search engines is always to provide the most relevant, high-quality results to users' queries.
Google gives some guidance on how to rank well in its organic search results, focusing on factors like backlinks, content freshness, keyword mentions, user experience, and topical authority.
I wrote a guide to how the Google Search Algorithm works for Ahrefs if you want to learn more. Otherwise, keep reading to get to the juicy bits!
Lesson 5: Keyword Research
The first part of gaining search engine rankings is keyword research. I'm putting Keyword Research before the "SEO basics" lesson for one reason:
You can do everything right and rank for a keyword... only to realize you chose a poor keyword and the traffic you're getting doesn't convert. Oops.
To avoid that, I want to make sure you know how to find awesome keywords and how to tell a great keyword from a steaming pile of useless garbage.
Step 1: Research Your Competitor's Keywords
I'll be honest: most free keyword research tools suck. They require you to do way too much work for less-than-ideal results.
It's much easier to use an SEO tool like Ahrefs or SEMrush to find high-quality keywords. (Not sure which tool to use? I do a full comparison of them here.)
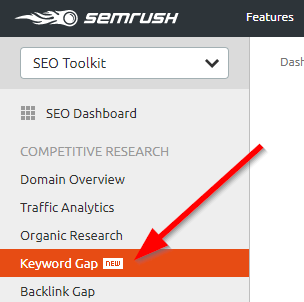
The method is the same with both tools — you use a feature called the "content gap" analysis. It essentially shows you the keywords that your competitors are ranking for but you aren't.
Note: If you don't yet have a website, you can still use competitors to find keyword ideas. So go through this process anyway.
Depending on which tool you're using, click the corresponding drop-down box below to learn how to find amazing keyword opportunities.
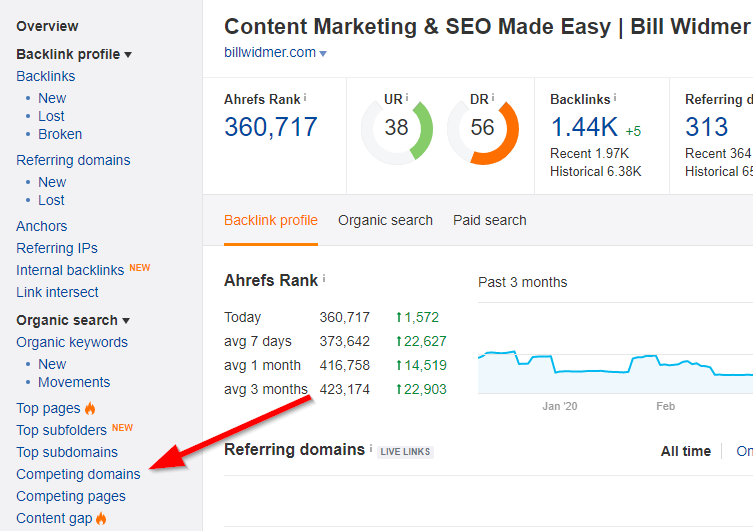
First, let's find your competitors. Head to the "Site Explorer" tool and plug in your URL.
Next, head to the "Competing Domains" tool in the left-hand menu under "Organic Search".
These are your top competitors according to who ranks for similar keywords as you. Copy-paste these URLs into a spreadsheet or notepad file.
If your site is still new and you don't have any rankings, this method won't work. Don't worry — you can still use Ahrefs for keyword research.
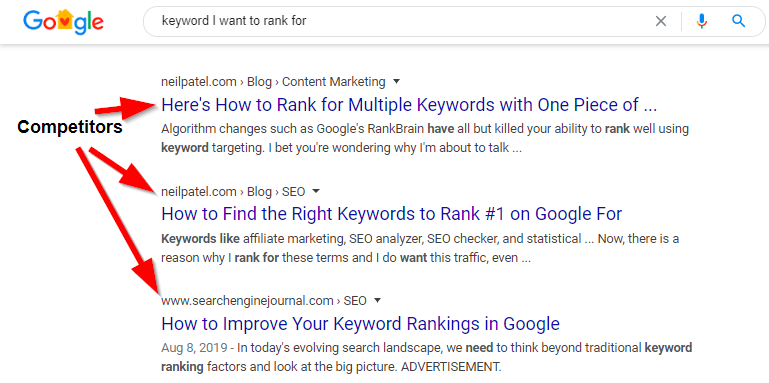
Just head over to Google and type in a keyword you think you'd like to rank for. The top pages ranking for that keyword are likely your competitors.
Now that you have your competitors URLs, it's time to use them for keyword research! Go back to your URL overview on Ahrefs and click the "Content Gap" tool in the left-hand menu under "Organic Search".
Paste 3-10 competing URLs into the empty boxes (the more the better) and click Show Keywords. Ahrefs will spit out hundreds, if not thousands of keywords that your competitors are ranking for that you're not!
Don't worry if this feels overwhelming — I'll show you how to trim this list down with filters and pick out the winners in step 2.
Step 2: Determine Which Keywords Are Worth Pursuing
Now that you have a massive list of keywords, how do you know which will bring you traffic that converts and which will bog your site down with worthless visitors?
Easy: Look at the cost-per-click (CPC), number of clicks, and what the current pages ranking are trying to get their visitors to do.
It takes practice to learn what a good keyword is and there's some nuance to it, so here's an example to show you the entire process.
Let's say you have a food blog as an example.
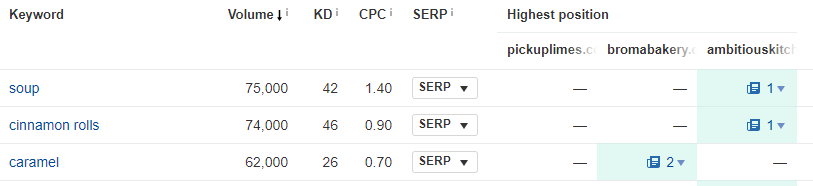
If we go through the process of finding keywords from competitors, here are a few I found:
These keywords are way too broad and too difficult to rank for. Unless you're a massive site like Food Network, good luck ranking for "soup".
So first, we need to filter these down a bit. I like to filter based on Keyword Difficulty (KD) and search volume.
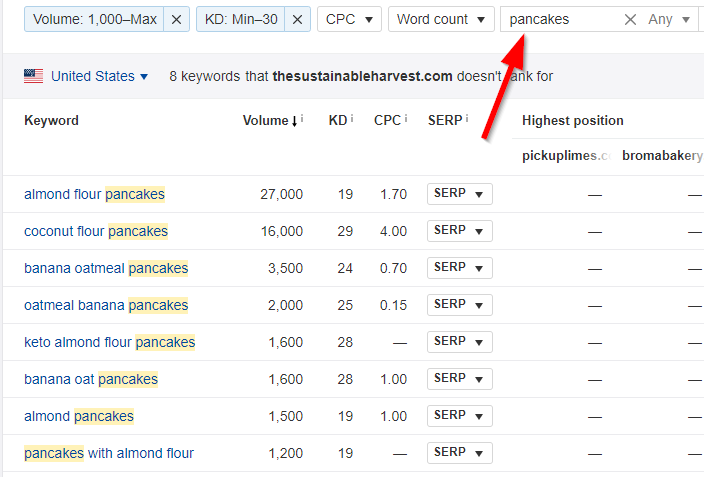
For this example, I'll filter by a KD of less than 30 and a volume of more than 1,000. This ensures you won't get any super difficult to rank for keywords.
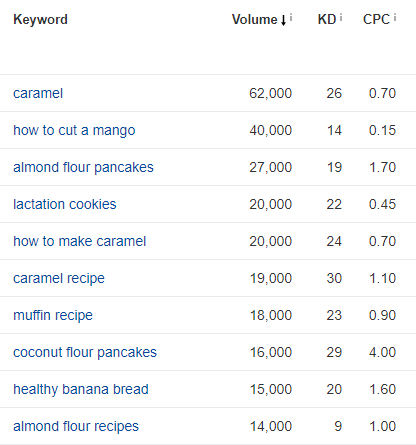
Here's what we have now:
Much better! Lots of good contenders here. Let's take a look at "coconut flour pancakes" because it has a high CPC of $4.00.
Here's the first result when we google that keyword:
It looks like she's selling pre-orders for her cookbook in order to monetize this keyword. If we scroll further down the page, I also noticed she uses the Amazon Affiliate Program to monetize.
Assuming you know how you're monetizing your own content, you should be able to calculate how much money you could potentially make from this keyword.
For example, this keyword gets 16,000 searches per month. On average, the #1 Google result gets ~35% of all the clicks, giving us ~5,600 visits per month if we were to rank #1 for "coconut flour pancakes".
(Note that this is assuming the page ONLY ranks for this one keyword, which is highly unlikely - you'll usually rank for dozens if not hundreds of keywords per page if you do search engine optimization properly!)
If you make $0.10 per visitor, on average, that would mean this keyword is worth $560 per month!
You could make a spreadsheet and use this calculation for every keyword you're considering ranking for to see how much each keyword is potentially worth. Then, add in the difficulty of each keyword to see income versus effort.
You're left with something like this:
*Click here to get a copy of this spreadsheet. It's free! I only ask that you share this guide 🙂
Just put in the keywords, KD and volume and it will give you your potential monthly income (assuming a #1 Google ranking and a $0.10 per visitor income).
If you make more or less, you can change the formula to whatever your income per visitor is, or do the calculations manually.
With this spreadsheet it's obvious which keyword to target first: Almond Flour Pancakes. With the lowest difficulty and highest potential monthly income, it's a no-brainer!
If you're observant, you may have noticed there are two keywords here that have to do with pancakes!
Lesson 6: The SEO Basics
Now that you understand how to find the best keywords to rank for, let's cover the search engine basics you need to know to get those rankings.
Put simply, search engine optimization involves three things:
- On-page SEO (creating and optimizing your content)
- Off-page SEO (building links)
- Technical SEO (site structure, site speed & schema)
I'm going to explain each of these in layman's terms that anyone could understand, so if anything sounds scary, don't worry! Just keep reading.
But first, we have to cover EEAT.
E-E-A-T
EEAT (or Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness and Trust) is part of Google's quality rater guidelines and arguably the most important thing to focus on when it comes to SEO in 2024.
In a nut shell, EEAT looks at:
- Whether the writer has any qualifications for what they are writing about
- If the website is authoritative (i.e. has backlinks from well-known sources)
- Whether the writer has experience with what they're writing about (shown through personal stories and examples, photos or videos of them doing what they're talking about or using the products they're reviewing, etc.)
- If the website is trustworthy (has a real business address and contact information, an SSL certificate, etc.)
To learn more about EEAT, I recommend watching this video:
On-Page SEO
On-page SEO, also called on-site SEO, covers everything related to content on your website. It mostly has to do with proper keyword placement.
Specifically, you want your target keyword to be included in:
- Your page title
- The URL of the page
- At least one header and/or subheader
- A few times in the body content of your page
- In the title and alt text of at least one image
Here's an infographic to help you visualize what this looks like:
Don't want to memorize all this? No problem — just get a plugin like Yoast SEO or SEOpress (I recommend SEOpress) and it will literally remind you to do these things and give you a green light when it's done.
In addition to ensuring proper keyword placement, you must have a great user experience as well. This means writing content that is easy to read and understand, formatted well with good use of images, bold/italics, and bulleted lists.
If you want to learn more about how I make sure my content is built for a great user experience as well as written for search engines, check out this guide!
Doing these things already puts you ahead of the competition. Feel free to go to the off-page SEO section now.
But if you REALLY want to rank and make that sweet passive income, I recommend going deeper and learning about LSI (latent semantic indexing) keywords as well as NLP (Natural Language Processing).
I promise you neither of these is as complicated as they sound. In fact, it's actually quite simple. But this is a "big brain" topic you can skip.
NLP is a way for Google to understand language and the subject of a page. It's similar to to LSI, but more advanced.
NLP seeks to understand the sentiment of a word or sentence. In other words, it wants to know whether a sentence is positive, negative, or neutral.
For example, "I hate shoes" is a negative sentiment, while "I love shoes" is a positive sentiment. This is overly simplified, but gets the point across.
Surfer SEO, the tool I mentioned to help you optimize your pages for LSI keywords, also has a new feature to help you identify NLP keywords as well as the best sentiment to use them with based on current search results.
If you want to learn more about NLP and how to use it to better optimize your pages for search engines, watch this webinar recording.
Off-Page SEO (Link Building)
Now that you understand on-page SEO, it's time to move off your website, aka off-page or off-site SEO.
While off-page SEO can include things like social media and advertising for brand awareness, the main thing you'll hear about (and by far the most important) is link building.
Link building is exactly what it sound like: building (or acquiring) links from other websites pointing to your website. Whenever you hyperlink text on your website to another site, that's a link. And that's what you want!
Now, link building is probably the most difficult part of SEO. But it's also one of the most important! You can target the best keywords and create the world's best search-optimized content, but if you don't build any links, you'll never rank.
In fact, only 7.4% of web pages have more than 3 backlinks. And that's the biggest reason most web pages never get any traffic from Google!
Think of links as votes for your website. The more votes you have, the better the chance Google will choose you to represent a given keyword.
Types of Links (Anchor Text)
Anchor text is the text the link is attached to.
There are 6 different types of anchor text you can get a link from:
- Exact-match anchor text: The text linking to your website perfectly matches the keyword you're trying to rank for. For example, if you're targeting "how to make money from home", the link looks like this: How to make money from home.
- Partial-match anchor text: The linked text partially matches the keyword you're targeting. So instead of "how to make money from home", the linked text might be something like "15 ways to make money from home" or "ideas for making money from home".
- Branded anchor text: The linking text is your brand name. For example, someone might link to one of my pages with the text "Bill Widmer".
- Naked link: There is no anchor text. Instead, it's the link itself, like this: https://billwidmer.com/
- Generic anchor text: The linking text is something generic, like "click here" or "this article".
- Images: Instead of text, an image is linked to the page.
Which is best, you ask? Well, the answer is: All of them!
There is no "golden ratio" of which types of links you want. While some SEOs theorize that your anchor text ratio should look as close as possible to what's currently ranking, I personally don't abide by that rule.
In general, exact-match anchor text has the strongest correlation with higher rankings, BUT too many can set off a red flag to Google and cause you to lose your rankings. This is to prevent people from just buying tons of exact-match links to abuse the system.
Personally, I aim for ~5-10% of my links to be exact-match (particularly from the higher domain authority sites) and the rest to be a mix of all the other anchor text types. In my opinion, the best policy is to just build links, try not to have too many exact-match, and not really worry about it too much.
How to Build Links
If there's one thing you should spend the majority of your time on when it comes to SEO, it's link building. Especially if you're a newer site with a low DA/DR.
But I can't teach you all of that in this one article or it would be even more massive than it already is! So to learn more about link building and how to do it, check out this article.
I also outline my exact link-building process (and much more) in my SEO case study.
Technical SEO
The last part of a good search strategy is technical SEO. No SEO for dummies guide is complete without it!
While you might think technical SEO mainly involves code, it's actually much simpler than that (usually).
Put simply, technical SEO includes your web page loading speed, URL structure, and navigation structure. It also covers your robots.txt file, XML sitemap, structured data/schema, SSL certificate, and breadcrumbs, among some other things.
Don't worry — it sounds much more complicated than it is and we'll break it down step-by-step. I don't know much about code and I'm not a very technical person, so if I can figure it out, so can you!
Here's what you need to know to create a search engine friendly site:
Google Search Console
If you haven't already set it up, go ahead and connect your site with Search Console. This is Google's official tool and you can do a lot of things here, including adding your robots.txt file and XML sitemap.
*Note that nearly all other search engines, such as Bing, also have their own search console you can connect with if you want to rank in additional search results.

Robots.txt
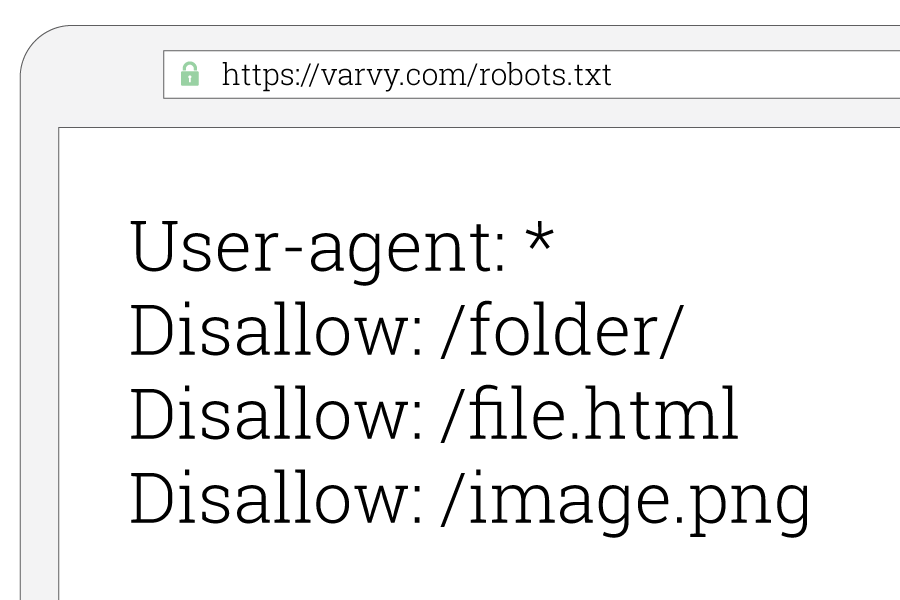
The Robots.txt file is a simple notepad file that tells Google which pages should and shouldn't be crawled and indexed in their search engine. It's easy to create and upload. Check out this guide to do it (it takes 5 minutes).
It can look like this, though yours may be slightly different:
XML Sitemap
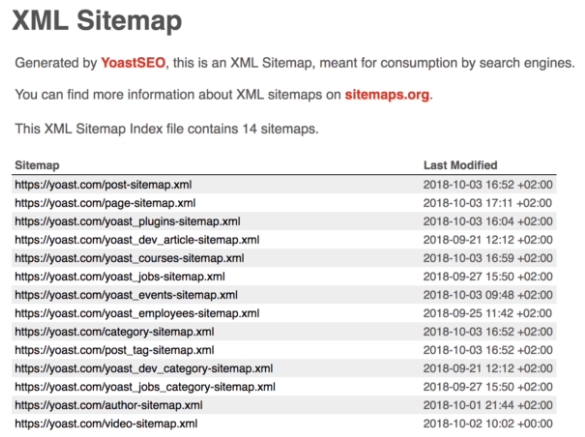
The XML sitemap file is a list of every single URL on your website to help search engines spiders crawl and navigate your site. If you're using WordPress, you can use Yoast SEO to create and upload your sitemap for free.
However, I much prefer and recommend the paid tool SEOpress, as it has more features and better security than Yoast. Aside from your XML sitemap and Robots.txt files, SEOpress can help you optimize your content, improve your load speed, add breadcrumbs, and much more.
Here's what your sitemap might look like:
You can also create a webpage version for users and search engines alike! You can see an example of this here. (Note: SEOpress will create and constantly update your webpage sitemap for you automatically once setup. Yoast SEO doesn't have that option.)
Website Loading Speed
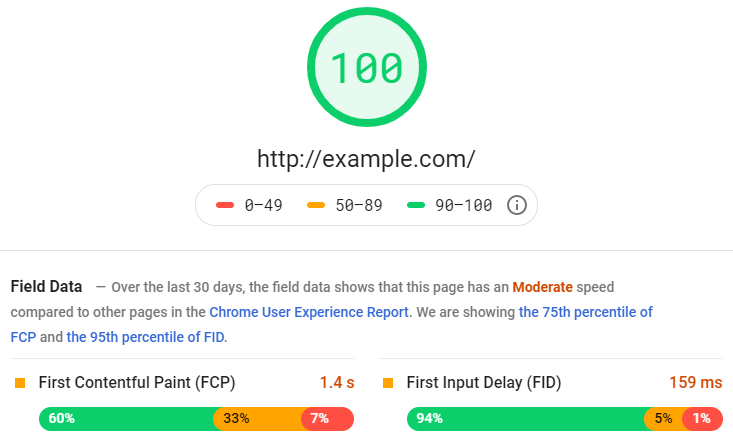
Your site's loading speed is important not just for search engines, but also for your users. In general, you want your pages to load in under 2 seconds. Ideally, you want a 1-second load speed, but this can be difficult to achieve.
To test your page's load speed, put your URL in Pingdom. It will show you your site's general loading speeds, along with any issues your page has and how to fix them.
But don't take their word for it. I recommend you also test your pages on Google's Page Speed tool as well, just to double-check.
There are a few super easy ways to improve your load speed. My first recommendation is to get better hosting!
If you're getting <10,000 visits per month, I recommend Siteground. They have fast, affordable hosting.
But if you're getting more traffic than that, then go with Kinsta! Kinsta is the hosting provider I currently use for everything, and they're lighting fast, have great customer service, and have lots of extra features like a free CDN (content delivery network) to further speed up your website.
Aside from hosting and a CDN, you can also improve load speed by compressing your images and improving your site's code. To learn more, check out this guide to website loadspeed.
SSL Certificate (HTTPS)
Last but not least, we can SSL security certificates! This is the "S" in "https" in your URL. It's what gives you the green lock in the URL bar:
It's important because without it, you likely will never show up in Google search results. Google basically made it mandatory, as without one, your visitors will get a "not secure" icon next to your URL, like this:
Seeing that is sure to hurt the user experience and make people leave!
Luckily, setting up SSL is free and easy to do. Most hosting providers give it to you with the click of a button. Here's how to do it with Siteground and here's how to do it with Kinsta.
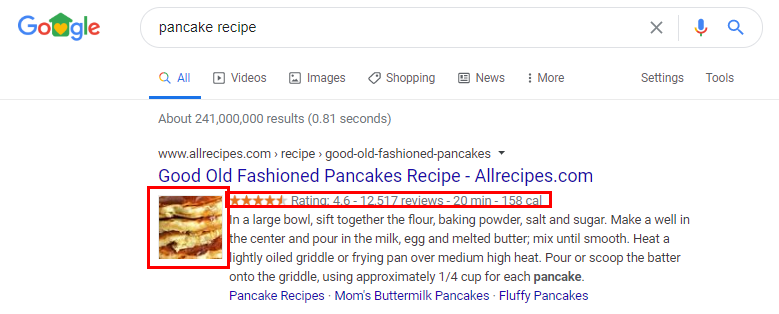
Structured Data (Schema)
Structured data is probably the most complicated part of technical SEO. And, while it is important and can help you, it's one of those "slight edge" tactics.
Meaning, you can and will rank without ever worrying about it, but it can be the difference between being the #1 result and the #2 result.
Basically, schema is extra code you add to a page to add features to your rankings such as product star ratings, recipe pictures, and the featured snippet that you often see when you Google something (see below).
Learning how to use structured data is beyond the scope of this guide, so if you want to learn it, I'll just refer you to this article.
And that's all I'm going to say about technical SEO in this guide! These are steps that anyone can take regardless of coding or technical knowledge, and are more than enough to get you ranking on search engines like Google.
That said, if you want to dive deeper, I recommend reading through this guide.
Lesson 7: How AI Will Impact SEO
It's 2024, and AI is on the rise. Since the release of ChatGPT in 2022, AI has become part of virtually every tool and software out there.
In fact, Google has recently released access to Bard, it's AI search companion and competitor to ChatGPT.
And Google also made a statement that it doesn't care if content is produced by AI, as long as it follows EEAT guidelines and is high-quality.
This pretty much means that if you want to stay competitive, you should embrace AI. My friend Jacob McMillen calls himself the "Cyborg Writer" and has a course on how to use AI to produce better content faster that can rank on Google.
SEO for Dummies: Conclusion
Search engine optimization doesn't have to be difficult or complicated. In the end, it boils down to finding the right keywords, creating great content, and building links to that content.
If you want to learn more about SEO and how to use it to make money, I highly recommend grabbing the Authority Site System by Authority Hacker. It's an extremely effective course that teaches you SEO and affiliate marketing.
If you're not interested in investing or simply can't afford it right now, they also have a free webinar that teaches you more about SEO as well.
That's all for my SEO for dummies guide! I hope you found it helpful!
Questions? Comments? Concerns? Drop a comment below and I'll get back to you ASAP! I read and respond to every single one!
Read Next: How to Optimize Your Airbnb Listing for Search Engines